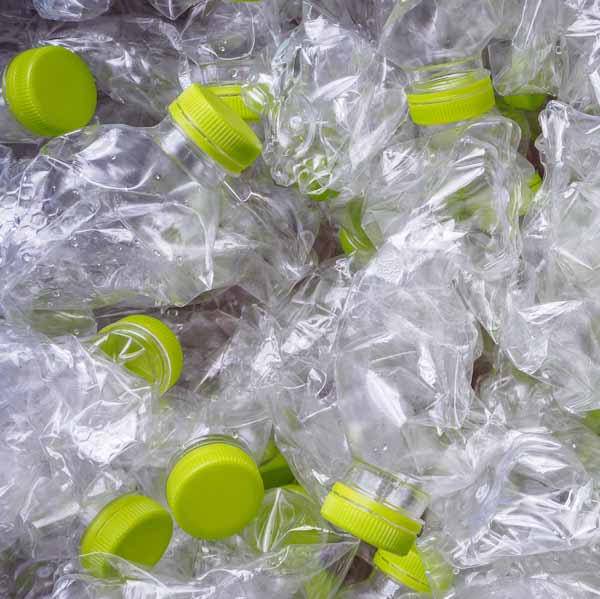
Sustainable plastics and polymers are materials that are designed to minimise their impact on the environment, both in terms of their manufacture and disposal. These materials typically have characteristics such as biodegradability, recyclability, and reduced use of non-renewable resources, which contribute to their overall sustainability.
Research in sustainable plastics and sustainable polymers is ongoing, with the aim of developing new materials with improved properties and reduced environmental impact. Efforts are being made to improve the recycling infrastructure and use of sustainable materials.
Eurofins offers testing services and solutions for sustainable plastics and polymer products across a range of industries including consumer products such as textiles, apparel, footwear and toys, cosmetics and personal care items, food and packaging.
Key topics in sustainable plastics and polymers
Biodegradable and Compostable plastics
These plastics are designed to break down naturally over time when exposed to the environment, usually through the action of microorganisms. Examples include polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), and polybutylene succinate (PBS).
Bio-based plastics
These plastics are made from renewable resources, such as plants or agricultural waste, instead of non-renewable fossil fuels. Common examples include PLA, which is derived from corn starch or sugarcane, and bio-based polyethylene (bio-PE), which is made from sugarcane or other plant sources.
Biocomposites
These materials combine natural fibers or fillers (e.g., wood, hemp, or flax) with a polymer matrix to create a composite material with improved mechanical properties and reduced environmental impact.
Environmentally degradable polymers
Some polymers, like polyolefin oxo-biodegradable plastics, are designed to degrade through oxidation followed by biodegradation under specific environmental conditions.
Recyclable plastics
These can be reprocessed and reused multiple times, reducing the need for new material production and waste generation. Examples include polyethylene terephthalate (PET), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and polypropylene (PP).
Recycled polymer content
Recycled polymer content regulations govern the minimum percentage of recycled materials required in the production of plastic products. It is therefore important to understand how many times plastics and polymers can be recycled and to verify the recycled content of products.
Per- and Polyfloroalkyl Substances (PFAS) free polymers
PFAS are often referred to as the “forever chemicals” as they take thousands of years to break down. Their bioaccumulative behaviour and toxicity mean they are becoming increasingly highly regulated with a need to provide evidence for compliance and find suitable PFAS-free polymer alternatives.
Sustainable chemistry
Designing plastics and polymers that minimise the use and generation of hazardous substances, reduce environmental impact, and promote the efficient use of resources, with the aim of contributing to a more sustainable and eco-friendly society.
- Microplastic testing
- Biodegradability and disintegration testing
- Compostability testing
- Ecotoxicity testing
- Bio-based content and certification
- Chem-ST hazardous chemical smart testing for all key global chemical restrictions
- Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) testing including Total fluorine (TF) and Total Organic Fluorone (TOF) as an indicator of PFAS contamination
- Zero waste to landfill certification
Contact us today to find out how we can help with sustainable plastics and sustainable polymers in your supply chain.
All Services
Industries supported
 Sustainable Chemical manufacturing
Sustainable Chemical manufacturing Sustainable Construction
Sustainable Construction Sustainable Cosmetics and Personal Care
Sustainable Cosmetics and Personal Care Sustainable cotton
Sustainable cotton Sustainable detergents
Sustainable detergents Sustainable Electrical and Electronics
Sustainable Electrical and Electronics Sustainable Farming
Sustainable Farming Sustainable Food
Sustainable Food Sustainable Footwear
Sustainable Footwear Sustainable Furniture
Sustainable Furniture Sustainable hygiene, paper and pulp
Sustainable hygiene, paper and pulp Sustainable Leather
Sustainable Leather Sustainable Paper and Packaging
Sustainable Paper and Packaging Sustainable Textiles
Sustainable Textiles Sustainable Toys
Sustainable Toys